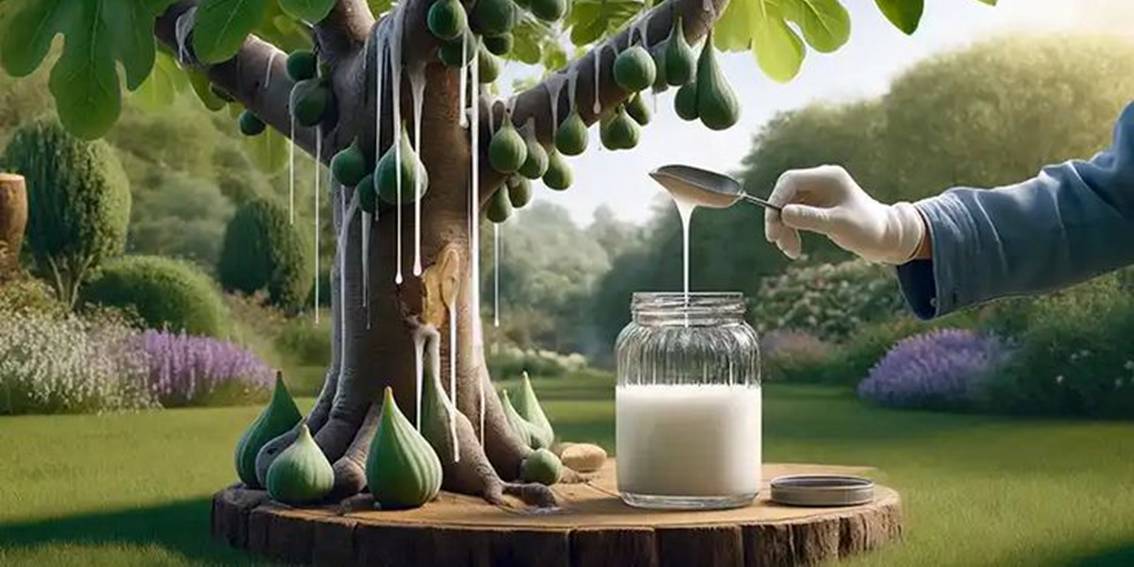
The Importance of Fig Sap
Fig sap, a milky secretion from the fig tree (Ficus spp.), holds significant value across various domains, including traditional medicine, modern pharmacology, and agricultural practices. This versatile substance has attracted attention due to its biochemical composition and diverse applications.
Traditional Medicinal Uses
Healers in many cultures have long utilized fig sap for its therapeutic properties. They apply it directly to warts, corns, and skin irritations due to its proteolytic enzymes, which help break down skin growths. Practitioners also use it to treat parasitic infections and digestive ailments by preparing decoctions or infusions. Indigenous knowledge continues to inspire modern research into its medicinal potential.
Pharmacological Potential
Researchers have conducted extensive studies on fig sap's chemical components, revealing promising pharmaceutical applications. Compounds such as ficin, a proteolytic enzyme, exhibit anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer properties. Scientists have tested ficin's ability to dissolve blood clots, offering potential in treating cardiovascular diseases. Laboratories have also explored its role in developing natural remedies for skin disorders, including psoriasis and eczema.
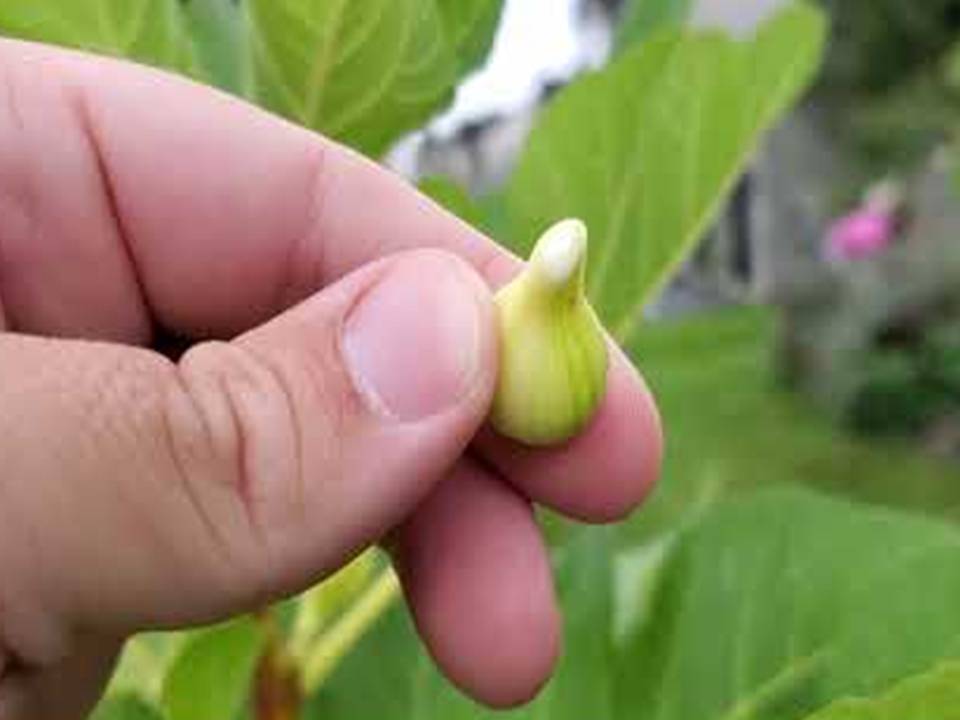

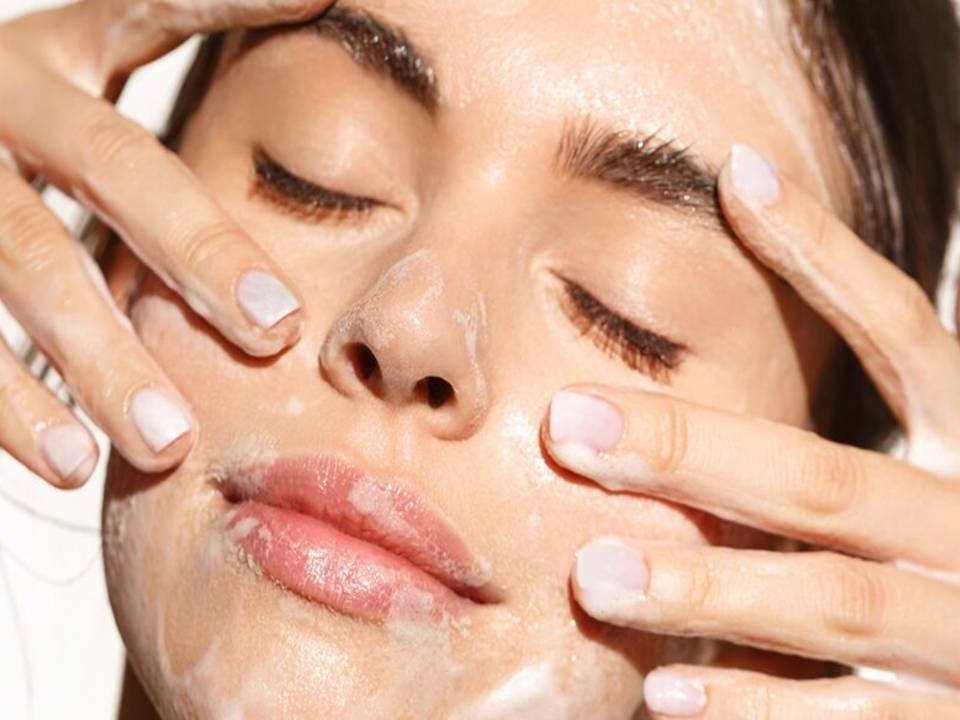
Cosmetic and Skincare Applications
The cosmetic industry incorporates fig sap into various skincare products. Companies value its natural exfoliating properties, using it in creams and serums to promote skin renewal. Formulators blend it into anti-aging products due to its ability to boost collagen production and improve skin elasticity. Consumers seeking natural and organic skincare alternatives increasingly prefer products containing fig sap.

Agricultural Benefits
Farmers and horticulturists recognize fig sap's utility in agriculture. They apply it as a natural pesticide, benefiting from its toxic effects on certain pests while posing minimal environmental risks. Growers also use it as a plant propagation aid, as the sap stimulates root development in cuttings. Sustainable agricultural practices continue to leverage this eco-friendly solution to reduce chemical pesticide reliance.
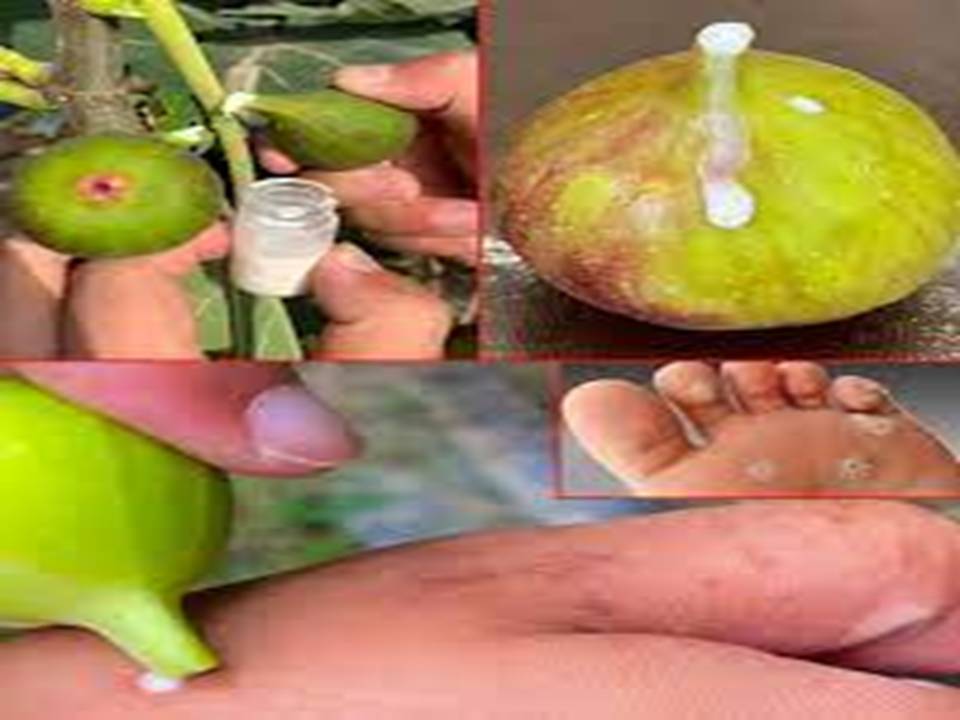
Cultural and Ritual Significance
Many cultures attribute symbolic and spiritual meanings to fig sap. Religious texts and folklore reference its protective and purifying properties. Communities use it in rituals and ceremonies, often associating it with fertility and abundance. This cultural reverence highlights its enduring presence in human history.

Challenges and Sustainability
Despite its benefits, harvesting fig sap presents challenges. Collectors must handle it cautiously because of its potential skin-irritating effects. Overharvesting can harm fig trees and disrupt ecosystems that depend on them. Conservationists advocate for sustainable harvesting practices to ensure long-term availability while protecting fig tree habitats.

Scientific Research and Future Prospects
Ongoing scientific research aims to unlock more of fig sap's potential. Biotechnologists explore its use in enzyme-based therapies, while pharmacologists test new drug formulations derived from its bioactive compounds. Environmental scientists study its role in sustainable agriculture and ecological restoration projects.
Conclusion
Fig sap embodies a unique blend of traditional wisdom and modern scientific promise. Its applications span medicine, cosmetics, agriculture, and cultural heritage. By balancing utilization with conservation, society can continue benefiting from this remarkable natural resource for generations to come.

Key Applications of Fig Sap:
1. Traditional Medicine:
Therapeutic Uses: Antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral properties.
Skin Treatments: Effective against warts, eczema, and fungal infections.
Wound Healing: Promotes tissue repair and reduces inflammation.
Chronic Disease Management: Antioxidants help manage oxidative stress and may assist in diabetes regulation.
2. Agriculture:
Natural Pesticide: Protects crops by repelling pests.
Herbicide Action: Controls weeds while being eco-friendly.
Plant Growth Enhancer: Contains enzymes that stimulate plant development.
3. Industrial Uses:
Rubber and Adhesives: Latex content supports the production of eco-friendly glues and sealants.
Cosmetics: Hydrating, exfoliating, and anti-aging properties make it valuable for skincare products.
Food Industry: Used in cheese-making as vegetarian rennet and as a natural sweetener in culinary products.
4. Environmental Conservation:
Ecosystem Support: Fig trees are keystone species, offering habitat and food for wildlife.
Sustainability Focus: Encourages environmentally responsible harvesting practices.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
Handling Precautions: Can cause skin irritation and allergic reactions.
Environmental Impact: Risks from overharvesting demand sustainable management.
Research Frontiers: Potential in cancer treatment, drug delivery, and improved industrial processes through biotechnology.
Fig sap's versatile applications and ecological significance underscore its role as a crucial resource. Balancing its extraction with conservation efforts will ensure its continued benefit for health, industry, and the environment.


